Chronic pain affects millions of individuals worldwide, prompting them to seek various treatment options to alleviate their discomfort and improve their quality of life. Among these options, prolotherapy and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy have gained popularity for their potential to provide long-term relief from chronic pain. However, as with any medical intervention, it’s crucial to consider the safety profiles and potential side effects of these treatments. In this comparative review, we’ll examine the safety and side effects of prolotherapy and PRP therapy for chronic pain management.
Safety Profile of Prolotherapy
Prolotherapy, also known as regenerative injection therapy, involves the injection of a solution, typically a dextrose-based substance, into damaged or weakened connective tissue and joints. While prolotherapy is generally considered safe, it’s essential to understand the potential risks associated with this treatment.
Studies evaluating the safety of prolotherapy have reported minimal adverse events and complications. Common side effects include temporary soreness or discomfort at the injection site, bruising, and mild swelling. These side effects typically resolve within a few days and are considered mild and transient.
In rare cases, more severe complications such as infection, nerve damage, or allergic reactions may occur. However, the incidence of such complications is extremely low when prolotherapy is performed by trained and experienced healthcare providers in a sterile clinical setting.
Safety Profile of PRP
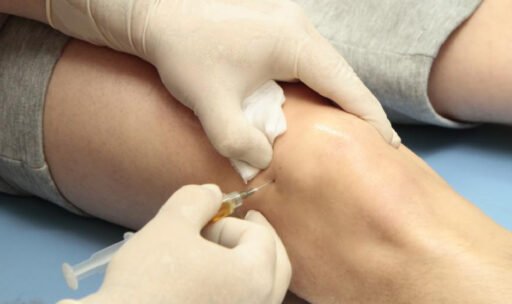
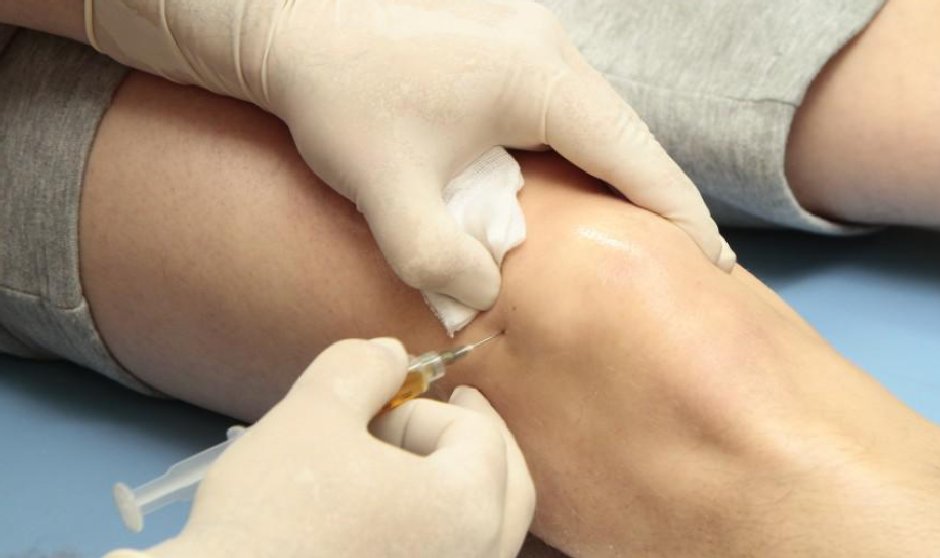
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy involves the extraction and concentration of platelets from the patient’s own blood, which are then injected into the affected area to promote tissue healing and regeneration. PRP therapy is generally considered safe, with a low risk of adverse events.
Studies investigating the safety of PRP therapy have consistently reported few complications. Common side effects include mild pain or discomfort at the injection site, bruising, and swelling. These side effects are usually temporary and resolve spontaneously within a few days.
Serious complications associated with PRP therapy, such as infection or nerve damage, are rare but may occur in some cases. However, the overall incidence of such complications is low when PRP injections are performed by qualified healthcare professionals using sterile techniques.
Comparative Analysis of Safety Profiles
When comparing the safety profiles of prolotherapy and PRP therapy, both treatments demonstrate a favorable safety profile with minimal risk of serious complications. Common side effects such as temporary discomfort or swelling are transient and generally well-tolerated by patients.
While both prolotherapy and PRP therapy carry a low risk of adverse events, it’s essential to recognize that individual patient factors and treatment variables may influence safety outcomes. Factors such as the skill and experience of the healthcare provider, the specific condition being treated, and the patient’s overall health may impact the safety and efficacy of both treatments.
Potential Side Effects of Prolotherapy
In addition to its safety profile, it’s essential to consider the potential side effects of prolotherapy. While rare, side effects such as infection, nerve damage, or allergic reactions may occur in some patients. However, the incidence of these side effects is extremely low when prolotherapy is performed by qualified practitioners using sterile techniques.
Potential Side Effects of PRP
Similarly, while PRP therapy is generally well-tolerated, there are potential side effects to consider. These may include temporary pain or discomfort at the injection site, bruising, or swelling. Serious complications such as infection or nerve damage are rare but may occur in some cases.
Comparative Analysis of Side Effects
When comparing the side effects of prolotherapy and PRP therapy, both treatments demonstrate a similar incidence of common side effects such as temporary pain or swelling at the injection site. Serious complications associated with both treatments are rare but may occur in isolated cases.
Safety Measures and Recommendations
To further optimize safety during prolotherapy and PRP therapy, healthcare providers should consider the following measures:
- Comprehensive Patient Evaluation: Before undergoing prolotherapy or PRP therapy, patients should undergo a thorough evaluation to assess their suitability for treatment. This evaluation may include a review of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging studies to identify any underlying conditions or contraindications.
- Customized Treatment Plans: Healthcare providers should develop individualized treatment plans based on patients’ specific needs and goals. Tailoring treatment to each patient’s unique circumstances can help minimize the risk of adverse events and optimize treatment outcomes.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are essential to track patients’ progress and monitor for any signs of complications. Healthcare providers should remain vigilant for adverse events and promptly address any concerns raised by patients.
- Patient Education and Informed Consent: Patients considering prolotherapy or PRP therapy should receive comprehensive education about the potential risks and benefits of treatment. This includes information about common side effects, rare complications, and alternative treatment options. Patients should be actively involved in the decision-making process and encouraged to ask questions and voice any concerns they may have.
- Preventive Measures: Healthcare providers should take proactive measures to minimize the risk of adverse events during prolotherapy and PRP therapy. This may include pre-procedural screening for allergies or underlying medical conditions, as well as the use of prophylactic antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications when indicated.
- Adherence to Sterile Techniques: Proper aseptic techniques are critical to reducing the risk of infection during prolotherapy and PRP therapy. Healthcare providers should adhere to strict sterile procedures when preparing and administering injections, including thorough hand hygiene, disinfection of injection sites, and the use of sterile gloves and equipment.
- Continuing Education and Training: Healthcare providers should stay updated on the latest research, guidelines, and best practices related to prolotherapy and PRP therapy. Continuing education and training can help ensure that providers are equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to deliver safe and effective care to their patients.
By implementing these additional safety measures, healthcare providers can further enhance the safety and effectiveness of prolotherapy and PRP therapy, ultimately improving patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both prolotherapy and PRP therapy offer valuable options for chronic pain management with favorable safety profiles and minimal risk of serious complications. While side effects such as temporary discomfort or swelling may occur with both treatments, these are generally mild and transient. Patients considering prolotherapy or PRP therapy should consult with a qualified healthcare provider to discuss their treatment options and develop a personalized treatment plan based on their individual needs and circumstances. By understanding the safety profiles and potential side effects of these treatments, patients can make informed decisions about their chronic pain management strategies. For more information on the comparative analysis of Prolotherapy vs. PRP for chronic pain relief, visit Selphyl.